Internet History Fun Facts
- A catalyst in the formation of the Internet was the heating up of the Cold War. The Soviet Union’s launch of the Sputnik satellite spurred the U.S. Defense Department to consider ways information could still be disseminated even after a nuclear attack.
- ARPANET was created in 1969 and provided the foundation for what came to be known as the Internet
- January 1, 1983 is the official birthday of the modern internet
OSI Model
The OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a telecommunication or computing system into seven abstraction layers. Each layer in the OSI model performs specific functions, and together they facilitate communication between different systems. Here’s a brief overview of what each layer does:
1. Physical Layer (Layer 1):
- Manages the physical connection and transmission of raw data bits.
2. Data Link Layer (Layer 2):
- Ensures reliable communication over a physical layer, handling framing and addressing.
3. Network Layer (Layer 3):
- Focuses on logical addressing and routing data between different networks.
4. Transport Layer (Layer 4):
- Manages end-to-end communication, ensuring reliable and ordered data delivery.
OSI Model in a network
1. Physical Layer (Layer 1):
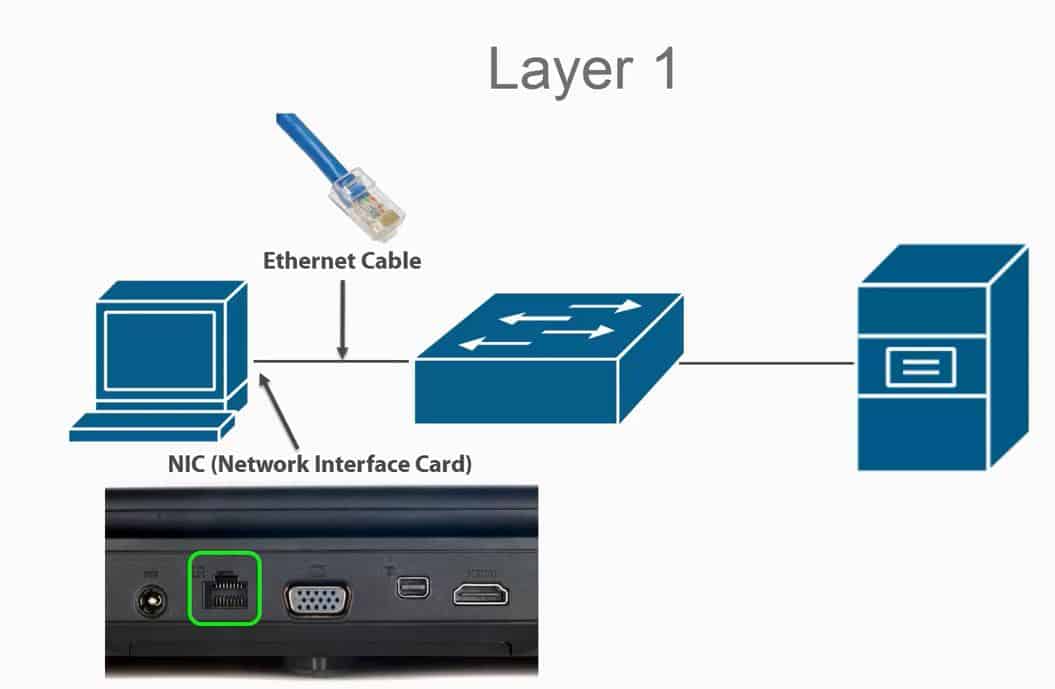
Layer 1 is how devices transmit information to each other (ethernet, network adaptors)
When we send information, we send it “physically” hence the name physical layer
2. Data Link Layer (Layer 2):
When we send information, we send it in binary, frames are the units of binary data, they are the information we send from one device to another (in the same network network)
For example, if i want to send the message “Hello” to my brother on the same network, the frame will be sent within the network to the corresponding MAC address(Media Access Control) address, sometimes referred to as a hardware or physical address, is a unique, 12-character alphanumeric attribute that is used to identify individual electronic devices on a network.
Frames can only be sent on the same network
A switch is a fundamental networking device that operates at the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) of the OSI model. Its primary function is to connect devices within the same local area network (LAN) and facilitate communication between them. Here’s how switches work and why they are crucial in network setups:

3. Network Layer (Layer 3):
If I wanted to play Valorant with a friend, I would need to connect to the WiFi, why?
Unlike frames, my friend is not on the same network as me, which means MAC Addresses aren’t enough to locate the device so they cannot communicate with eachother
So we need to identify Hanlun Li on a specific network, how do we do that? IP addresses
IP Addresses are supposedly a unique identifier for each device on the network, to access a seperate device on the network, we must give a destination IP address.
Packets are basically just frames, but with an IP address included in them
4. Transport Layer (Layer 4):

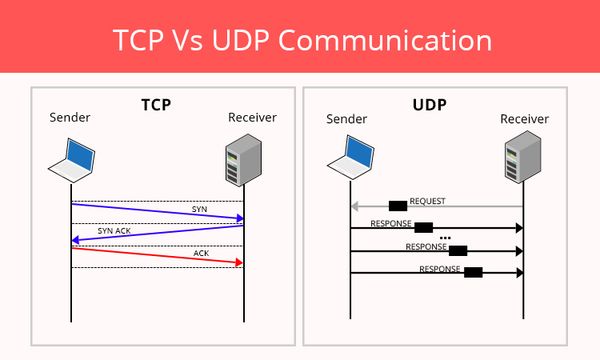
Layer 4 has two protocols UDP and TCP, you can think of it as UDP you just spam packets to the other network without acknowledgement whereas TCP you need to acknowledge everything sent to the other network.
In other words, TCP is slower but more reliable, while UDP is faster but less reliable
For example:
If I’m sending an important email to my boss, I would use TCP because I wouldn’t want the data to be corrupted or lost.
But, If I’m playing a FPS game, I would use UDP because I need speed to load in whats happening within the game
Application Layer (Layer 7)
The Application Layer is the topmost layer in the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a telecommunication or computing system into seven abstraction layers. The Application Layer (Layer 7) is the layer closest to end-users and provides network services directly to applications.
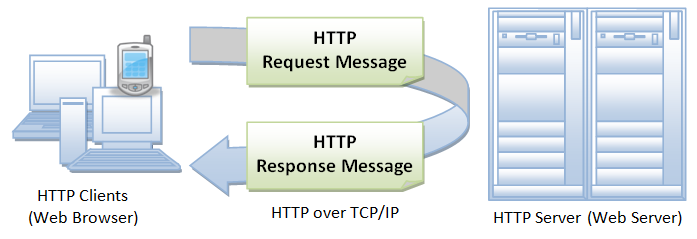
- HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol):
- Used for transmitting hypertext (web pages) on the World Wide Web.
- Supports the communication between web browsers and web servers.
- HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure):
- Similar to HTTP but uses a secure SSL/TLS connection for encrypted communication.
- Used for secure online transactions, login pages, and sensitive data transfer.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol):
- Facilitates the transfer of files between computers on a network.
- Allows for the upload and download of files.
- DNS (Domain Name System):
- Resolves domain names to IP addresses.
- Essential for translating human-readable domain names to machine-readable IP addresses.

- SSH (Secure Shell):
- Provides a secure, encrypted channel for remote access to devices.
- A more secure alternative to Telnet.
1. Physical Layer (Layer 1) Example:
- Scenario: Transmitting data over an Ethernet cable.
- Functionality:
- Manages the physical connection between devices.
- Handles the transmission of raw data bits over the Ethernet cable.
- Deals with aspects like cable types, connectors, and signal modulation.
Key Terms:
Ethernet
Data Link Layer (Layer 2) Example:
- Scenario: Communication between two computers over an Ethernet network.
- Functionality:
- Breaks data into frames with start and stop bits for accurate transmission.
- Manages MAC addresses for unique identification of devices.
- Regulates frame flow to prevent network congestion.
- Implements error-checking mechanisms like checksums or CRC for data integrity.
Switches
Network Layer (Layer 3) Example:
- Scenario: Routing data between two networks.
- Functionality:
- Focuses on logical addressing to uniquely identify devices on different networks.
- Determines optimal paths for data to travel from the source to the destination.
- Manages communication between networks using routers.
- Provides a foundation for end-to-end communication across interconnected networks.
Routers - How frames are encapsulated into packets
IPV4 Addresses/IPV6 Addresses - Unique Identifiers on Internet
Transport Layer (Layer 4) Example:
- Scenario: Ensuring reliable communication between two applications.
- Functionality:
- Manages end-to-end communication, ensuring data arrives reliably and in the correct order.
- Provides error detection and recovery mechanisms for data integrity.
- Uses protocols like TCP for connection-oriented and reliable communication.
- Supports protocols like UDP for connectionless and faster communication when some data loss is acceptable.
Transport Layer (Layer 4) - TCP vs. UDP
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- Scenario: Reliable communication requiring guaranteed data delivery.
- Functionality:
- Establishes a connection between sender and receiver before data transfer.
- Ensures reliable and ordered delivery of data.
- Implements error detection and correction mechanisms.
- Well-suited for applications where data integrity is crucial, such as file transfers and web browsing.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- Scenario: Faster communication with acceptable data loss.
- Functionality:
- Connectionless protocol without establishing a connection before data transfer.
- Does not guarantee reliable or ordered delivery of data.
- Suitable for real-time applications like video streaming and online gaming, where speed is prioritized over perfect data transmission.
- Minimal overhead, making it more lightweight than TCP.
TCP and UDP are two different approaches to data transport, each suited to specific application requirements. The choice between them depends on the priorities of the application: reliability (TCP) or speed (UDP).
Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs):
- What does the Data Link Layer (Layer 2) focus on in a network?
- a. Logical addressing
- b. Physical addressing
- c. Network routing
- d. Transport protocols
- Which device operates at the Data Link Layer and uses MAC addresses for forwarding frames?
- a. Router
- b. Hub
- c. Switch
- d. Repeater
- In networking, what does a MAC address uniquely identify?
- a. Devices on the same network
- b. Devices on different networks
- c. IP addresses
- d. Subnets
- What is the main function of switches in a network?
- a. Logical addressing
- b. Frame forwarding
- c. IP addressing
- d. Network routing
- Which layer of the OSI model deals with physical transmission, like Ethernet and network adaptors?
- a. Network Layer (Layer 3)
- b. Physical Layer (Layer 1)
- c. Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
- d. Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- What does Layer 3 (Network Layer) use for unique device identification between different networks?
- a. IP addresses
- b. MAC addresses
- c. Port numbers
- d. Subnet masks
- Which protocol operates at Layer 4 and ensures reliable communication by acknowledging data receipt?
- a. UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
- b. HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- c. TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
- d. DNS (Domain Name System)
- What is the main difference between UDP and TCP in Layer 4?
- a. TCP is faster but less reliable.
- b. UDP is slower but more reliable.
- c. TCP acknowledges data receipt, while UDP doesn’t.
- d. UDP is used for emails, and TCP for gaming.
- In a network, what does the Transport Layer manage?
- a. Physical transmission
- b. MAC addresses
- c. Traffic flow between networks
- d. Framing of data
- Why would you choose UDP over TCP for a real-time application like online gaming?
- a. UDP is more reliable.
- b. TCP is faster.
- c. UDP provides faster communication.
- d. TCP ensures every message is acknowledged.
ANSWER KEY
ƃuᴉssǝɹppɐ ʅɐɔᴉsʎɥԀ .q :ɹǝʍsu∀
ɥɔʇᴉʍS .ɔ :ɹǝʍsu∀
ʞɹoʍʇǝu ǝɯɐs ǝɥʇ uo sǝɔᴉʌǝᗡ .ɐ :ɹǝʍsu∀
ƃuᴉpɹɐʍɹoⅎ ǝɯɐɹᖵ .q :ɹǝʍsu∀
(⇂ ɹǝʎɐ⅂) ɹǝʎɐ⅂ ʅɐɔᴉsʎɥԀ .q :ɹǝʍsu∀
sǝssǝɹppɐ ԀI .ɐ :ɹǝʍsu∀
(ʅoɔoʇoɹԀ ʅoɹʇuoϽ uoᴉssᴉɯsuɐɹꓕ) ԀϽꓕ .ɔ :ɹǝʍsu∀
.ʇ╻usǝop ԀᗡՈ ǝʅᴉɥʍ ʻʇdᴉǝɔǝɹ ɐʇɐp sǝƃpǝʅʍouʞɔɐ ԀϽꓕ .ɔ :ɹǝʍsu∀
sʞɹoʍʇǝu uǝǝʍʇǝq ʍoʅⅎ ɔᴉⅎⅎɐɹꓕ .ɔ :ɹǝʍsu∀
.uoᴉʇɐɔᴉunɯɯoɔ ɹǝʇsɐⅎ sǝpᴉʌoɹd ԀᗡՈ .ɔ :ɹǝʍsu∀
HW: Answer all HW questions with a line of reasoning
WILL BE GRADED ON ACCURACY AND REASONING
- b. Physical addressing: When we send information, we send it “physically” hence the name physical layer
- c. switch : Manages MAC addresses for unique identification of devices. Regulates frame flow to prevent network congestion.
- a. Devices on the same network: Manages MAC addresses for unique identification of devices.
- b. Frame Forwarding: Routers - How frames are encapsulated into packets
- b. physical layer: Manages the physical connection and transmission of raw data bits.
- a. IP addresses: Focuses on logical addressing and routing data between different networks.
- c. TCP (transimission control protocol): Manages end-to-end communication, ensuring reliable and ordered data delivery.
- c. TCP acknowledges data reciept, while UDP doesn’t: Layer 4 has two protocols UDP and TCP, you can think of it as UDP you just spam packets to the other network without acknowledgement whereas TCP you need to acknowledge everything sent to the other network. In other words, TCP is slower but more reliable, while UDP is faster but less reliable
- c. Traffic Flow between networks:
- c. UDP provides faster communication







